Avoiding the trigger, however, can make anxiety worse in the long term. Treatment can help you overcome the need to avoid a trigger.
It’s important to understand that anxiety disorders can be treated, even in severe cases. Although anxiety usually doesn’t go away, you can learn to manage it and live a happy, healthy life.
Anxiety is a normal part of being human. But for some, it is always there and too much to handle. It can be a nagging fear of daily life or a worrisome concern before a big test, and anxiety can damage both body and emotions. In this guide, we will explore what anxiety is, its triggers, and effective techniques for dealing with it.
What is Anxiety? What Causes It?
Anxiety is the way your body responds to stress. It typically manifests as worry or nervousness when you are dealing with situations such as interviews, public speaking, or major decisions. For most individuals, these feelings disappear once the stressful situation has passed.
But if worry continues—longer than six months—and disrupts daily life, it can be a sign of an anxiety disorder. Therefore, it is extremely crucial to learn to manage anxiety.
When Anxiety Turns into a Mental Health Problem?
It is normal to feel nervous at times. But with anxiety disorder, you constantly worry and fear, which interferes with your daily life. This affects your work, relationships, or family life.
Those living with anxiety disorders may avoid certain places or situations entirely. In severe cases, individuals may struggle to leave their homes or maintain social connections. Without proper support or treatment, anxiety often intensifies over time.
The American Psychiatric Association indicates that anxiety disorders are the most prevalent emotional disorders and may occur at any age. Females have a higher likelihood of diagnosis compared to men.
Types of Anxiety Disorders You Should Know
Anxiety varies from person to person. There are many forms of anxiety disorders, including:
Panic Disorder – Recurrent, unpredictable panic attacks with intense fear of another.
Specific Phobias – An intense fear of specific things such as spiders, flying, or heights.
Social Anxiety Disorder– Overwhelming fear of being judged or embarrassed in public.
Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder (OCD)– Unwanted and recurring thoughts and behaviors based on unreasonable fears.
Separation Anxiety – Fear of separation from those you care about.
Illness Anxiety Disorder– Inordinate worry about being sick (previously referred to as hypochondria).
Anxiety can be a comorbid condition with the following:
- Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder (PTSD)
- Major Depressive Disorder
- Chronic illnesses (e.g., diabetes, COPD)
- Substance abuse
- Chronic pain issues
- Inflammatory diseases (such as arthritis)
Common signs of anxiety to monitor
Anxiety touches every individual differently. Some experience physical pain, whereas others experience emotional or mental ailments. These are some of the most typical symptoms:
- Constant worrying or having rapid thoughts
- Restlessness or irritability
- Difficulty concentrating or feeling mentally fatigued
- Sleep disturbances, such as insomnia or nightmares
- Chest pain or churning nausea
- Muscle tightness or chest pain
- Severe anxiety can also lead to panic attacks.
What Occurs During a Panic Attack?
A panic attack is the sudden onset of intense fear or discomfort peaking in minutes. These symptoms are some of the following:
- Chest pain or pressure
- Shortness of breath
- Nausea or dizziness
- A sense of losing control or fear of death.
- Chills, hot flashes, or sweating
- Tingling sensation in hands or feet
Recurring panic attacks are suggestive of panic disorder and merit assessment by a mental health counselor.
Primary Causes of Anxiety: Why Does It Occur?
Certain internal and external sources may contribute to the creation of anxiety. They are:
- Chronic stress
- Hereditary predisposition
- Chemical imbalances in the brain
- History of trauma or abuse
- Chronic health conditions
- Drug abuse
- Personal or high-pressure work environments
The cause can be used to determine the optimal treatment.
Who will be most nervous?
Everyone can get anxious, but some are more prone to doing so because of:
- Shyness or unsociability in early childhood
- Trauma or serious life stressors
- Anxiety or mental health problems in family history
- Physical health issues like hormone disorders
- Too much caffeine or stimulants
How Do Experts Diagnose Anxiety?
There is no one test to diagnose anxiety. Rather, clinicians typically employ an extensive process that is comprised of:
- Routine check-ups and laboratory studies to rule out health-related etiologies
- Psychological testing and mental health screening
- Symptom checklists and ratings of behavior
- A mental health specialist will discuss how your symptoms affect your daily life in assessing an accurate diagnosis.
Treating Anxiety: Options, Medications, and Natural Care
The good news is that anxiety is treatable. The majority of individuals fare better with a mix of medical and non-medical approaches:
1. Psychotherapy (Talk Therapy)
The best method is Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT). It helps in altering anxious thoughts and teaches efficient coping skills.
I’d like you to please read the CBT guide for more information.
2. Prescription Drugs
Physicians may prescribe SSRIs or other antidepressants. They even prescribe short-term anti-anxiety medications such as benzodiazepines, but their long-term use is discouraged as it causes dependence.
3. Holistic and Complementary Approaches
Mindfulness, yoga, journaling, and breathing exercises decrease stress daily and optimize emotional health.
Good Habits to Overcome Daily Worries
Forming daily routines decreases anxiety naturally. Here are some tips for your life:
- Regularly exercise to reduce stress hormones
- Sleep first for improved mood and energy
- Consume a well-balanced diet
- Restrict caffeine, alcohol, and nicotine
- Be aware and meditate
- Stay in touch with useful people
Natural Supplements and Remedies to Ease Anxiety
Most individuals seek out natural means to assist their mental well-being. Some of the popular options include:
- Ashwagandha – May lower cortisol levels (stress hormone).
- Chamomile tea – Encourages relaxation and peacefulness
- Lavender essential oil – Facilitates reducing anxiety in aromatherapy.
- B vitamins and magnesium – Essential for maintaining the nervous system.
Note: Alternative treatments should supplement, not substitute for, professional treatment.
Identifying Anxiety in Youth and Teenagers
They may also be worried. An anxiety disorder affects about 1 in 10 young people aged 3 to 17 years. Symptoms may include:
- Mood change or irritability
- School and social avoidance
- Sleep disturbances
- Frequently getting headaches or stomachaches
- Early intervention, particularly cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT), can help children learn coping skills and enhance their resilience.
The Effects of Alcohol on Anxiety
Others consume it to feel better, but it is harmful to them. Even though alcohol will make one feel a little better initially, it worsens anxiety later on and makes one dependent.
It is important to treat anxiety and substance use simultaneously for long-term recovery.
Can Food Alleviate Anxiety Symptoms?
Mental health relies significantly on a healthy diet. Certain foods can help alleviate anxiety symptoms by affecting brain chemistry, reducing inflammation, and improving gut health. These foods tend to induce good feelings:
- Fatty fish (such as salmon) for omega-3 fatty acids.
- Turmeric with curcumin for brain health.
- Dark leafy greens are rich in magnesium.
- Flax and chia seeds are healthy sources of fats and fiber.
- Food items containing Vitamin D, such as eggs or fortified food.
- Sources of tryptophan (like turkey and oats) to help make serotonin.
Stopping Anxiety in Its Tracks: Early Interventions That Work
Prevention of chronic anxiety can reduce the risk, particularly in youth. Successful techniques are:
- School mental health programs
- Conflict resolution training and anti-bullying
- Open communication and supportive parenting
- Early intervention through family counseling
- Building a protective and supportive environment is crucial for maintaining emotional well-being.
- Simple and Convenient Tools to Support Anxiety.
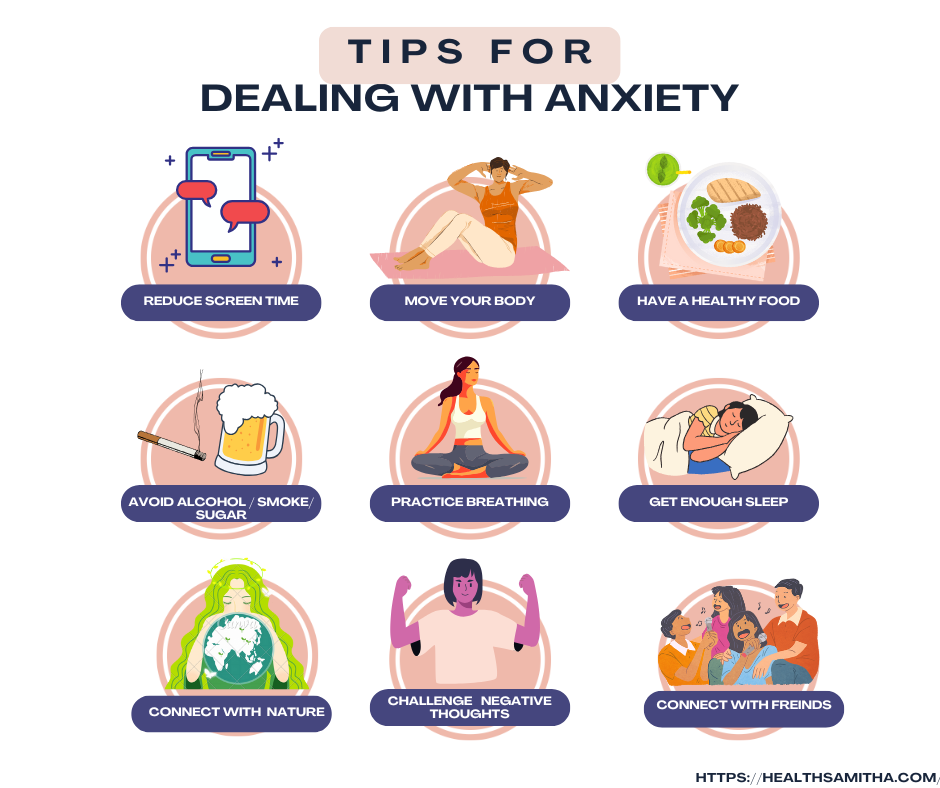
Simplify things by incorporating these simple, day-to-day tactics to master anxiety:
- Deep breathing exercises
- Grounding techniques, including the 5-4-3-2-1 technique
- Positive affirmations to become confident
- Setting healthy boundaries
- Divide big tasks into smaller steps Belonging to a peer support group.
Last Words: You Can Defeat Anxiety.
Anxiety is a part of life, but it is not a part to dominates life. With appropriate support from experts, self-care measures, and natural remedies, you can conquer anxiety and live a blissful life. Doing it ahead of time, being consistent, and being open to experimenting with new approaches are the fundamentals of handling anxiety effectively. You can always bounce back—begin today.
Nice guide, good pointers